The most common causes of lumbar pain are spinal diseases, mainly degenerative-district (osteochondrosis, spondylosis deformities) and back muscle overload.Moreover, various diseases of the abdominal and pelvis organs, including tumors, can cause the same symptoms as a hernia disc that compresses the spinal root.
It is no coincidence that such patients turn to not only neurologists but also for gynecologists, orthopedists, urologists and, of course, to local or family doctors.
The etiology and pathogenesis of lumbar pain
According to modern ideas, the most common causes of lumbar pain are:
- Pathological changes in the spine, mainly degenerative-district;
- pathological changes in muscle, most often myofascial syndrome;
- pathological changes in the abdominal organs;
- Nervous system diseases.
Risk factors for lumbar pain are:
- severe physical activity;
- unpleasant behavior of work;
- damage;
- cooling, drafts;
- alcohol abuse;
- depression and stress;
- Professional diseases associated with exposure to high temperatures (in particular, in hot stores), radiation energy, sudden temperature fluctuations and vibrations.
Among the vertebral causes of lumbar pain are:
- root ischemia (discogenic radical syndrome, discogenic radiculopathy), which comes from root compression from a disc hernation;
- Reflex muscle syndromes, the cause of which can be degenerative changes in the spine.
Disordishes different functional disorders of the lumbar spine can play a certain role in the appearance of back pain, when, due to incorrect behavior, blocks of intervertebral joints occur and their movement is damaged.At the joints located above and below the block, compensating hypermobility develops, leading to muscle spasm.
Signs of acute compression of the spinal canal
- numbness of the perineal area, weakness and numbness of the legs;
- maintaining urination and defects;
- With the compression of the spinal cord, there is a decrease in pain, followed by a feeling of numbness in the pelvic band and limbs.
Lumbar pain in childhood and adolescence is often caused by abnormalities in the development of the spine.Spinal Bifida (Spina Bifida) occurs in 20% of adults.After examination, hyperpigmentation, birth signs, multiple wounds and skin hyperkeratosis in the lumbar region are detected.Sometimes urinary incontinence, trophic disorders and weakness in the legs.
Lumbar pain can be caused by lumbarization - the transition of vertebra s1 with respect to the lumbar spine - and sacralization - connecting vertebra L5 to the sacrum.These abnormalities are formed due to the individual characteristics of the development of transverse processes of the vertebrae.
Nosological forms
Almost all patients complain of pain in the lower back.The disease is mainly manifested by inflammation of the low -movement joints (intervertebral joints, costovertebral, lumbosacral) and spinal ligaments.Gradually, the oses develops in them, the spine loses elasticity and functional mobility, becomes like a bamboo stick, fragile and easily injured.At the stage of pronounced clinical manifestations of the disease, chest mobility during respiration and, as a result, the vital ability of the lungs decreases significantly, which contributes to the development of a number of pulmonary diseases.
Spinal cord
A distinction is made between benign and malignant tumors, mainly originating in the spine and metastatic.Benign spine tumors (osteochondrome, chondromes, hemangiomas) are sometimes asymptomatic clinical.With hemangioma, a spinal fracture can also occur with minor external influences (pathological fracture).
Malignant tumors, mostly metastatic, derive from prostate, uterus, breast, lungs, adrenal glands and other organs.Pain in this case occurs much more often than with benign tumors - usually persistent, painful, intensifying with the slightest movement, depriving patients from rest and sleep.It is characterized by a progressive deterioration of the condition, an increase in general exhaustion and significant changes in the blood.X -rays, calculated tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are of great importance for diagnosis.
Osteoporosis
The main cause of the disease is a decrease in the function of the endocrine glands due to an independent disease or against the background of general aging of the body.Osteoporosis can develop in patients taking hormones, aminazine, anti-tuberculosis and tetracycline medicines for a long time.Disordishes Radicular disorders associated with back pain arise due to deformation of intervertebral foramine, and spinal disorders (myelopathy) arise due to compression of the radiculomedular artery or vertebral fracture, even after minor injuries.
Myofascial syndrome
Myofascial syndrome is the leading cause of back pain.It can be due to overexertion (during severe physical activity), overlap and muscle bruise, non -physiological behavior during work, response to emotional stress, shortening one foot and even flat legs.
Myofascial syndrome is characterized by the presence of so -called "trigger" areas, the pressure on which it causes pain, often radiating in neighboring areas.In addition to myofasic pain syndrome, the cause of the pain can also be inflammatory muscle disease - myosite.
Lumbar pain often occurs due to diseases of the internal organs: stomach and duodenum ulcers, pancreatitis, cholecystitis, urolithiasis, etc.They can be pronounced and imitated the lumbosacral lumbago or discogenic radiculitis figure.However, there are also clear differences, thanks to which it is possible to distinguish the pain referred to from what derives from the diseases of the peripheral nervous system, which is due to the symptoms of the underlying disease.
Clinical symptoms of lumbar pain
Most often, lumbar pain occurs between the ages of 25 and 44.There is acute pain, which last, as a rule, 2-3 weeks, and sometimes up to 2 months, and chronic pain - over 2 months.
Radicular compression syndromes (discogy radiculopathy) are characterized by a sudden onset, often after severe rise, sudden movements or hypothermia.Symptoms depend on the location of the lesion.The occurrence of the syndrome is based on root compression by a hernia disc, which occurs as a result of degenerative processes facilitated by static and dynamic loads, hormonal disorders and damage (including spinal microtraumatization).Most often, the pathological process includes spinal root areas from the dura material to the intervertebral foramen.In addition to disc herniation, bone growth, scar changes in epidural tissue, and hypertrophized flavum ligament can be included in root trauma.
The upper roots of the lumbar (L1, L2, L3) are rarely affected: they make up no more than 3% of all lumbar radicular syndromes.Root L4 is affected twice as often (6%), causing a characteristic clinical appearance: mild pain along the lower and anterior inner surface of the thigh, the medial surface of the foot, paresthesia (sensation of numbness, burning, crawling) in this area;Easy weakness of the quadrilateral muscle.Knee reflexes are stored and sometimes increased.The L5 root is most commonly affected (46%).The pain is located in the lumbar and gluteal regions, along the outer surface of the thigh, the anterial-out surface of the lower leg and fingers III-V.It is often associated with a decrease in the sensitivity of the skin of the outer side surface of the foot and in the strength in the extensor muscles of the third to fifth fingers.The patient finds it difficult to stay on his heel.With long radiculopathy, the hypotrophy of the anterial muscle tibialis develops.The S1 root is also often affected (45%).In this case, the pain in the lower back radiates along the outer surface of the thigh, the outer surface of the foot and lower leg.The examination often detects the hypalges of the outer rear surface of the foot, the reduction of the triceps muscle strength and the toe flexors.It is difficult for such patients to stay on their fingers.There is a decrease or loss of Achilles reflex.
Vertebrogenic lumbar reflex syndrome
May be acute or chronic.Acute lumbar pain (LBP) (lumbago, "lumbago") occurs within minutes or hours, often suddenly due to difficult movements.Piercing, the purpose (as an electric shock) The pain is localized throughout the lower back, sometimes radiating into the iliac region and buttocks, intensifies severely when coughing, sneezing and decreases when stretched, especially if the patient finds a comfortable position.Movement in the lumbar spine is limited, the lumbar muscles are tense, causing the symptom of lasegue, often bilateral.Thus, the patient lies on the back with elongated legs.The doctor simultaneously bends the affected leg in the knee joints and hip.This does not cause pain because with this position of the foot, the diseased nerve is calm.Then the doctor, leaving the leg bent at the hip-femoral joint, begins to fix it in the knee, causing tension in the sciatica, which gives it severe pain.Acute lumbodynia usually lasts 5-6 days, sometimes less.The first attack ends faster than the subsequent ones.Repeated Lumbago attacks tend to develop in chronic LBP.
Atypical lower back pain
There are a number of clinical symptoms that are atypical for back pain caused by degenerative changes in the spine or myophassic syndrome.These signs include:
- the appearance of pain in childhood and adolescence;
- spine damage just before the onset of back pain;
- back pain associated with fever or signs of intoxication;
- spine;
- rectum, vagina, both legs, band pain;
- Linking back pain with eating, defective, sexual intercourse, urination;
- Non -ecological pathology (amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea, vaginal discharge), which appeared against the background of lower back pain;
- Increased pain in the lower back in a horizontal position and decreased in a vertical position (the symptom of razdolsky, characteristic of a tumor process in the back);
- continuous growth pain over one to two weeks;
- limbs and appearance of pathological reflexes.
Exam methods
- external examination and palpation of the lumbar region, identification of scoliosis, muscle tension, pain and causing points;
- Determination of the range of movement in the lumbar spine, muscle loss areas;
- examination of neurological status;Determination of tension symptoms (Lassegue, Wasserman, Neri).[Wasserman's symptom study: leg bending at the knee joint in a patient in a prone position causes pain in the thigh.Neri's symptom study: sharp curvature of the head in the chest of a patient lying on the back with straight feet causes acute pain in the lower back and along the sciatica.];
- study of the state of sensitivity, sphere of reflex, muscle tone, vegetative disorders (swelling, color changes, fever and moisture of the skin);
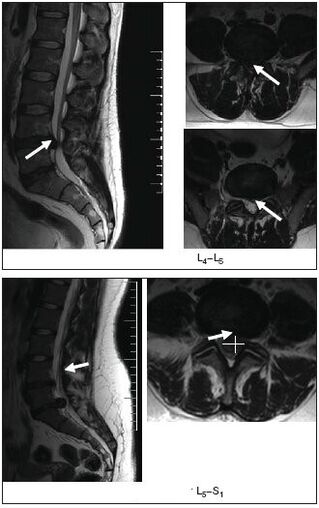
- Radiography, computer or magnetic back resonance.
MRI is particularly informative
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs;
- gynecological examination;
- If necessary, additional studies are performed: cerebrospinal fluid, blood and urine, sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy, gastroscopy, etc.
Treatment
Acute back pain or deterioration of vertebral or myofasic syndromes
Undifferentiated treatment.Soft motor way.In case of severe pain in the early days, resting the bed, and then walking into crutches to discharge the spine.The bed should be difficult, and a wooden board should be placed under the mattress.For warmth, a wool scarf, an electric heating pillow and light sand bags or salt are recommended.Ointments have a beneficial effect: Finalgon, Tiger, Capsin, Diclofenac, etc., as well as mustard plaster and pepper plaster.Ultraviolet radiation in erymic doses, caterpillars (considering potential contraindications) and irrigation of the painful area with ethyl chloride are at risk.
Electrical procedures have an analgesic effect: transcutaneous electroanalgesia, modulated sinusoidal currents, diadean currents, electrophoresis with novocaine, etc.The use of reflexology (acupuncture, laser therapy, cauterization) is effective;Novokaine blockade, pressure massage of causing points.
Medication therapy includes analgesics, NSAIDs;soothing and/or antidepressants;Drugs that reduce muscle tension (muscle relaxants).In the event of arterial hypotension, tizanidine should be described very carefully because of its hypotensive effect.If swelling of the spinal roots is suspected, diuretics are described.
The main analgesic drugs are NSAIDs, which are often used uncontrollably by patients when the pain intensifies or repeated.It should be noted that long -term use of NSAID and analgesic increases the risk of complications of this type of therapy.Currently, there is a large selection of NSAIDs.For patients suffering from back pain, due to availability, effectiveness and lower likelihood of side effects (gastrointestinal bleeding, dyspepsia), "non-sector" medicines are diclofenac 100-150 mg/day.Orthize, intramuscularly, locally concentrated, ibuprofen and oral ketoprofen 200 mg and topically, and among those "selective" - oral meloxicam 7.5-15 mg/day, orally 200 mg/day nimesulide.
When treating with NSAIDs, side effects can occur: nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, pain in the epigastric region.Possible ulcerative effect.In some cases, ulcers and bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract may occur.In addition, headaches, dizziness, drowsiness and allergic reactions (skin rashes, etc.) are observed.Treatment is contraindicated for ulcerative processes in the gastrointestinal tract, pregnancy and breastfeeding.To prevent and reduce dyspeptic symptoms, it is recommended to take NSAIDs during or after meals and drink milk.Moreover, taking NSAIDs when the pain grows along with other medicines the patient takes to treat concomitant diseases, leads, as it is observed in the long -term treatment of many chronic diseases, in a decrease in adhesion of treatment and, as a result, insufficient effectiveness of therapy.
Therefore, modern methods of conservative treatment include the mandatory use of medicines that have chondroprotective, contaminating effects and have a better therapeutic effect than NSAIDs.Teraflex-Advance drugs fully meets these requirements, which is an alternative to NSAID for mild to moderate pain.A teraflex-advance drug capsule contains 250 mg of glucosamine sulfate, 200 mg chondroitin sulfate and 100 mg ibuprofen.The chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine participate in connective tissue biosynthesis, helping to prevent cartilage destruction processes and regeneration of stimulating tissue.Ibuprofen has analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects.The mechanism of action occurs due to selective cyclooxygenase blockage (COX Types 1 and 2), the main enzyme in the metabolism of arachidonic acid, which leads to a decrease in prostaglandins synthesis.The presence of NSAIDs in the composition of the Theraflex-Advance drug helps to increase the range of movement in the joints and reduce the morning rigidity of the joints and spine.It should be noted that, according to R.J.Tallida et al., The presence of glucosamine and ibuprofen to the Theraflex advantage provides synergism regarding the analgesic effect of the latter.Moreover, the analgesic effect of the combination of glucosamine/ibuprofen is provided by a dose of 2.4 times lower ibuprofen.
After relieving the pain, it is reasonable to switch to taking Teraflex drug, which contains the active ingredients chondroitin and glucosamine.Teraflex is taken 1 capsule 3 times a day.During the first three weeks and 1 capsule 2 times a day.in the next three weeks.
The vast majority of patients receiving positive dynamics in the form of pain relief and a decrease in neurological symptoms.The drug was well tolerated by patients, no allergic manifestations were observed.The use of teraflex for degenerative spine disease is rational, especially in young patients, both in combination with NSAIDs and both monotherapy.In combination with NSAIDs, the analgesic effect occurs 2 times faster, and the need for therapeutic doses of NSAIDs decreases progressively.
In clinical practice, for peripheral nervous system lesions, including those associated with spinal osteochondrosis, B vitamins, which have a neurotropic effect, are widely used.Traditionally, the alternatively administration method of vitamins B1, B6 and B12, 1-2 ml each is used.intramuscular with everyday alternation.The course of treatment is 2-4 weeks.The disadvantage of this method include the use of small doses of drugs, which reduces the effectiveness of Treatment and the Need for Frequent Injections.
For discogenic radiculopathy, attractive therapy is used: traction (including under water) in a neurological hospital.For myofascial syndrome, after local treatment (Novokaine blockade, ethyl chloride irrigation, anesthesia ointments), a hot compress is applied to the muscles for several minutes.
Chronic lumbar pain of vertebrogen or myogenic origin origin
In case of disc herniation, it is recommended:
- wearing a solid corset like "weightlifting belt";
- avoiding sudden movements and bending, restricting physical activity;
- physical therapy to create a muscle corset and restore muscle mobility;
- massage;
- Novokaine blockade;
- Reflexology;
- Physiotherapy: ultrasound, laser therapy, heat therapy;
- Intramuscular vitamin therapy (B1, B6, B12), multivitamins with mineral supplements;
- For paroxysmal pain, carbamazepine is prescribed.
Medication -free treatment
Despite the availability of effective means of conservative treatment, the existence of dozens of techniques, some patients require surgical treatment.
Indications for surgical treatment are divided into relative and absolute.The absolute story of surgical treatment is the development of caudal syndrome, the presence of a sequestrated intervertebral disc, severe radical pain syndrome that does not decrease despite treatment.The development of radiculomyeloischemia also requires urgent surgical intervention, however, after the first 12-24 hours, indications for operations in such cases become relative, first, due to the formation of irreversible changes in the roots, and secondly, because in most cases, during measures of treatment and rehabilitation, the process of regression.The same regression periods are observed with delayed operations.
Relative indications include failure of conservative treatment and repeated sciatica.Conservative therapy should not exceed 3 months in duration.and last at least 6 weeks.It is assumed that a surgical approach in cases of acute radical syndrome and conservative treatment failure is justified within the first 3 months.After the onset of pain to prevent chronic pathological changes in the root.A relative indicator is cases of extremely severe pain syndrome, when the component of pain is replaced by an increase in neurological deficit.
Among the physiotherapeutic procedures, electrophoresis with the proteolytic enzyme Caripination is currently widely used.
It is known that physical therapeutic training and massage are an integral part of the complex treatment of patients with spinal lesions.Therapeutic gymnastics follows the goals of the overall strengthening of the body, enhancing efficiency, improving coordination of movements and increasing fitness.In this case, special exercises are intended to restore some motor functions.


















